The Science of Camera Placement — How Angles, Height, and Light Decide What AI Sees
Security camera placement determines what your AI truly sees. Learn the science behind lenses, height, and lighting — and how ArcadianAI’s Ranger adapts to every environment for precision surveillance.
- Introduction
- Quick Summary / Key Takeaways
- Background & Relevance
- 1 | Lens Engineering: How Optics Shape AI Vision
- 2 | Lighting Physics and Lux Management
- 3 | Height and Angle: Geometry of Intelligence
- 4 | Placement by Environment
- 5 | Environmental Interference
- 6 | Connectivity & Power
- 7 | Compliance & Privacy
- 8 | Common Mistakes (Reverse Psychology Edition)
- 9 | How ArcadianAI Ranger Compensates
- 10 | Comparison Table
- 11 | Frequently Asked Questions
- 12 | Conclusion & Call to Action
- Security Glossary (2025 Edition)
(Last updated: October 2025)
Introduction
Most integrators obsess over camera brands, megapixels, and NVR capacity.
Few stop to ask the one question that decides everything: “What does the camera actually see?”
According to Statista (2025), more than 1 billion security cameras are now deployed globally, yet law-enforcement data shows that over 40 % of recorded incidents produce footage that is unusable — blurred, backlit, or blocked.
The culprit isn’t bad hardware. It’s geometry.
A camera angled 10 degrees too high misses faces. One mounted 3 meters too low floods the lens with headlights.
Even the best AI analytics — Verkada, Genetec, Milestone, Eagle Eye Networks — cannot analyze what physics obscures.
That’s why ArcadianAI built Ranger, a camera-agnostic, AI-as-a-Guard engine that adapts to suboptimal layouts, learning context across multiple cameras, lighting states, and seasons.
This article decodes the science of camera placement, from lens optics to environmental lighting, so that every pixel counts.
Quick Summary / Key Takeaways
-
Placement defines the intelligence of every frame.
-
Height, angle, and lens choice determine AI confidence scores.
-
Lighting direction matters more than resolution.
-
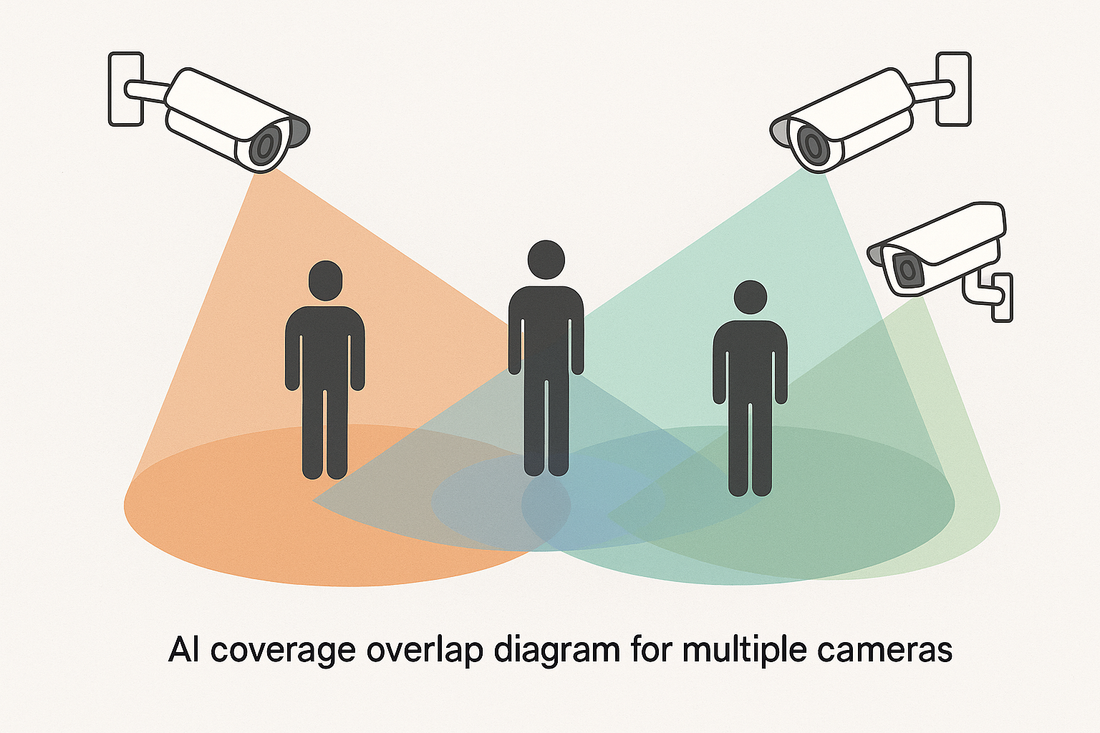
Overlap between cameras prevents “blind donuts.”
-
ArcadianAI Ranger adapts to imperfect placements through dynamic visual reasoning.
Background & Relevance
The global video-surveillance market surpassed USD 58 billion (2025), yet fewer than 15 % of systems are optimized for analytics accuracy.
Every analytic model — object detection, intrusion, face recognition — depends on pixel quality.
A 4K sensor at a bad angle can perform worse than a 1080p sensor placed scientifically.
Pixel density rule of thumb:
-
40 pixels/ft (130 px/m) → facial recognition
-
20 pixels/ft (65 px/m) → behavior detection
-
10 pixels/ft (33 px/m) → motion classification
If mounting height or field-of-view (FoV) violates this ratio, detection confidence drops up to 70 %.
1 | Lens Engineering: How Optics Shape AI Vision
| Lens Type | Typical Focal Length | Horizontal FoV | Ideal Use Case | Example Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wide Fixed | 2.8 mm | 100–120° | Lobbies, retail, classrooms | Hanwha PNV-A6081R, Axis M3086-V |
| Mid Range | 4–6 mm | 70–90° | Entrances, corridors | Uniview IPC2325EBR5-DPZ28, Hikvision DS-2CD2147G2-LU |
| Telephoto | 8–12 mm | 20–40° | License plates, gates | Axis Q1700-LE, Hanwha XNO-9083R |
| Varifocal | 2.8–12 mm | Variable | Mixed environments | Dahua N52AFA2 series |
| PTZ | 4.3–129 mm | 2–80° | Stadiums, parking lots | Hanwha XNP-9250RH |
Key physics:
-
Shorter focal length → wider FoV, lower detail.
-
Longer focal length → narrow FoV, higher detail.
-
Sensor size (1/1.8″ > 1/2.8″) improves low-light performance.
-
Aperture (f/1.4–f/2.8) controls depth of field; wider aperture = better night detail but more blur risk.
-
Lens distortion (barrel or pincushion) bends straight edges, confusing object-tracking AI.
2 | Lighting Physics and Lux Management
Lux Reference Table
| Environment | Typical Lux | AI Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Moonlight night | 0.1 | IR only; limited contrast |
| Street illumination | 10 | IR washout risk |
| Office indoor | 300–500 | Flicker, mixed color temp |
| Warehouse | 100–200 | Shadows from racks |
| Sunny day | 10 000 + | Backlight saturation |
Core rules:
-
Avoid direct sunlight into lens; it causes ghosting and false motion.
-
IR LEDs can over-expose at < 2 m — tilt up 5–10°.
-
Use cameras with WDR ≥ 120 dB (Axis P32 series) for glass-door entrances.
-
AI performs best when exposure variance < 30 %.
ArcadianAI Ranger dynamically learns lighting transitions (day/night, dusk/dawn) to maintain stable detection thresholds.
3 | Height and Angle: Geometry of Intelligence
| Scenario | Mount Height (m) | Tilt Angle (°) | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail checkout | 2.5–3 | 15–25 down | Capture faces & hands |
| Parking lot | 3.5–5 | 25–35 | Read plates, see perimeter |
| Warehouse | 6–9 | 35–45 | Cover vertical racks |
| School hallway | 2.7 | 10–20 | Identify faces, avoid glare |
| Construction pole | 4–6 | 20–30 | Detect intrusion, reduce sway blur |
Mathematical insight:
FoV = 2 × arctan (sensor width / (2 × focal length))
Pixel per foot = (horizontal pixels) ÷ (scene width ft)
4 | Placement by Environment
Retail & Convenience
-
Position near 3 m height for face visibility.
-
Avoid dome glare from refrigerators.
-
Cross-cover POS counters for skip-scan analytics.
-
Example setup: Hanwha XNV-8083R + ArcadianAI Ranger for behavioral correlation.
Parking & Automotive
-
Mount 3.5–5 m height, 20° tilt.
-
Use telephoto (8–12 mm) for plate recognition.
-
IR reflection off wet asphalt → enable WDR and polarizer.
-
Axis Q1700-LE and Hanwha PNO-A9081R are benchmarks.
Apartments / Condos
-
Cover stairwells at mid-height (2.7 m) for facial ID.
-
Avoid door glass reflection; use side-angle mount.
-
Ranger correlates lobby + parking to follow person-of-interest across feeds.
Industrial & Warehousing
-
Account for vibration; use anti-shock mounts.
-
Lighting: 4000 K LEDs recommended for color fidelity.
-
Dust or humidity → IP66 housing minimum (e.g., Hikvision DS-2CD2T86G2-4I).
Schools & Daycares
-
Respect privacy lines: avoid bathrooms and nap zones.
-
Ideal height ≤ 3 m to recognize teachers vs students.
-
Ranger’s context model prevents false “aggression” alerts during play.
Mobile CCTV Trailers
-
6–7 m mast; wind sway tolerance ±3°.
-
Ranger’s temporal correction stabilizes frame interpretation.
-
4G/5G uplink → minimum 3 Mbps per camera.
5 | Environmental Interference
| Condition | Optical Effect | AI Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rain / Snow | Refraction, blur | Object merge errors | Hydrophobic coating, hoods |
| Fog | Contrast loss | Low confidence scores | Thermal overlay |
| Heat wave | Shimmer | False motion | Temporal smoothing |
| Wind vibration | Jitter | Bounding box drift | Mount stabilizer |
| Seasonal glare | Over-exposure | Shadow ghosting | WDR + auto iris |
6 | Connectivity & Power
| Type | Uplink Bandwidth | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| PoE wired | Stable 100 Mbps+ | Power + data in one cable | Max 100 m distance |
| Wi-Fi | Varies 10–50 Mbps | No cable | Signal loss, latency |
| 4G/5G | 5–20 Mbps avg | Mobile sites | Data costs |
| Fiber | 1 Gbps+ | High reliability | Expensive install |
For 1080p @ 15 fps (H.264), allocate ≈ 2–4 Mbps uplink.
Ranger compresses metadata, streaming only when meaningful activity occurs — cutting bandwidth 40 – 70 %.
7 | Compliance & Privacy
Camera angles define legal exposure zones.
-
NDAA: avoid banned chipsets (Hikvision/Dahua OEM).
-
PIPEDA / GDPR: ensure FoV excludes private dwellings.
-
SOC 2 / PCI: mask POS terminals displaying credit data.
ArcadianAI anonymizes imagery beyond retention policy while preserving analytic metadata.
8 | Common Mistakes (Reverse Psychology Edition)
-
Mounting in corners: creates circular blind zones.
-
Ceiling fisheyes everywhere: wide but blind underneath.
-
Too high mount: “surveillance from space” = no faces.
-
Relying on megapixels: pixel density ≠ clarity.
-
Ignoring light direction: the cheapest camera facing north beats the best one facing sunset.
-
Trusting software to fix physics: AI needs visibility, not miracles.
9 | How ArcadianAI Ranger Compensates
-
Visual Context Learning: Adapts to light, shadow, and reflection.
-
Cross-Camera Correlation: Re-identifies events across angles.
-
Dynamic Sensitivity: Adjusts motion thresholds by zone.
-
Multi-Frame Reasoning: Understands motion patterns vs random noise.
-
False-Alarm Reduction: Documented 30–65 % drop in pilots.
-
Case Fusion Pipeline: Observer → Alerter → Case Manager for contextual alerts.
10 | Comparison Table
| Parameter | Static VMS | Proprietary VSaaS (Verkada / Genetec) | ArcadianAI Ranger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera control | Fixed FoV | Limited digital zoom | Adaptive scene understanding |
| False-alarm filter | Motion only | Basic AI | Contextual AI (−65 %) |
| Hardware dependency | High | Medium | Camera-agnostic |
| FoV compensation | Manual | Partial | Multi-camera logic |
| Privacy filtering | Static mask | Basic zones | Dynamic region masking |
| ROI Timeline | > 18 mo | 12–18 mo | 6–9 mo |
11 | Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What’s the ideal height for face clarity?
Around 2.5–3 m indoors, angled 15–25 ° down.
Q2. Do 4K cameras improve AI detection?
Only if pixel density is maintained and lighting is stable.
Q3. Color vs IR — which is better for AI?
Color for day, IR for night; Ranger auto-balances based on confidence.
Q4. Can AI fix poor placement?
It can compensate ≈ 30 – 40 % via context, but physics still wins.
Q5. Should I mix brands?
Yes — Ranger is camera-agnostic and analyzes ONVIF/RTSP feeds equally.
Q6. How often should I re-calibrate?
Twice a year or after major layout/lighting changes.
12 | Conclusion & Call to Action
Perfect placement turns hardware into intelligence.
Even imperfect setups become powerful when AI understands geometry.
ArcadianAI Ranger bridges both worlds — blending physics, optics, and adaptive reasoning.
Because true security isn’t about seeing more cameras.
It’s about seeing more meaning.
Security Glossary (2025 Edition)
Aperture (f-stop): Lens opening that controls light entry.
Blind Spot: Area not captured within FoV.
CMOS Sensor: Light-sensitive chip that creates the image.
Dynamic Range (WDR): Ability to handle dark + bright areas.
Field of View (FoV): Horizontal scene width captured.
False Positive: AI flag of non-incident.
IR Cut Filter: Switches between day color and night IR.
Lux: Unit of illumination (measure of light intensity).
Multi-Camera Correlation: AI linking events across feeds.
NDAA: U.S. security compliance restricting certain hardware.
NVR / VMS / VSaaS: Recording and management systems.
Object Detection Confidence: AI’s probability that a classification is correct.
Pixel Density: Pixels per foot or meter of scene.
PoE: Power over Ethernet cabling standard.
PTZ: Pan-Tilt-Zoom camera type.

Security is like insurance—until you need it, you don’t think about it.
But when something goes wrong? Break-ins, theft, liability claims—suddenly, it’s all you think about.
ArcadianAI upgrades your security to the AI era—no new hardware, no sky-high costs, just smart protection that works.
→ Stop security incidents before they happen
→ Cut security costs without cutting corners
→ Run your business without the worry
Because the best security isn’t reactive—it’s proactive.